 What is PMIS(Project Management Information System)?
What is PMIS(Project Management Information System)?PMIS is the abbreviation of the network-based project management information system developed independently by our company. According to the setting of project basic data and the collection and processing of project data, data sharing can be realized between project managers and projects. At the same time, through the workflow settings, the command drivers related to development tasks among project members are realized.
 PMIS Function Structure
PMIS Function Structure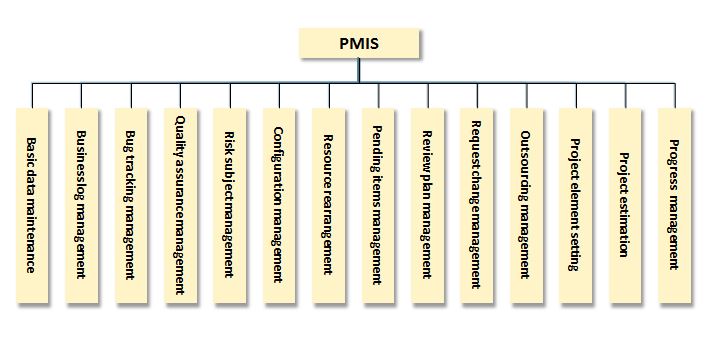
Here is some function introduction of some modules.
 Project Element Setting
Project Element Setting This module is used to set the basic data of the project. It mainly includes the setting or change of basic data such as "basic information setting", "function setting", "system setting", etc.
This module restricts the access rights of project members by security restrictions, access rules and so on, based on the information of the organization, membership position and role within the system.
 Buziness Log Management
Buziness Log Management This module manages detailed work status of all developers. It mainly has functions such as "registration", "approval", "search" and "statistics" of the business diary.
The work time of each task and function is divided into P(plan), D(design or coding), C(check or review), A(fault repair or update), and R(report/contact/interview) to register in the business log. The system sends reminder mail to people who forget to register every day. Supervisors can approve or reject the logs, but if rejected, the reasons must be entered to prompt the daily revision. Furthermore, if the supervisor does not approve it on time, the system will send a reminder email.
For the classification and statistics of work-hour data, the corresponding grouping conditions can be set for different analysis purposes, which is helpful for the pre-analysis of various working hours, help for the work-hours analysis of task classification, and the work-hours analysis of quality management.
 Bug Tracking Management
Bug Tracking ManagementThis module supports tracking all bug information found during project development, starting from invoice to resolution. It can manage the bugs found in test process, the bugs and accusations found in review process and the bugs found in debugging process with a unified way.
Once the bug is invoiced, the system will immediately send a notification email to the resolver, which will help solve the problem in the fastest time. If the expression of defect phenomenon is not clear or non-defect is identified, it can also be refused.
This module provides quality statistics such as error statistics classified by function, error correction classified by cause of occurrence, error statistics of occurrence engineering comparison and discovery engineering, etc. for the management and analysis of project quality status. However, if want to make deeper analysis, such as judging and identifying the cause of error detection engineering, the original error data can be exported to CSV file, which is helpful for the further analysis of artificial quality.
 Quality Assurance Management
Quality Assurance Management This module supports the management of defects that violate the development procedures. In view of the violation errors of the development procedures, the quality assurance procedure is followed from defect invoice to resolution
The corresponding priority of the blame vote is divided into high, medium and low. When the expected end date is exceeded, the system not only sends out a reminder, but also sends a blame notice to its superiors if the number of reminders is limited. Thus, it can reduce the problems that are delayed due to human factors.
In addition, statistical data for quality assurance can also be provided here.
 Risk Subject Management
Risk Subject Management This module has the function of identifying, analyzing and monitoring risks, so as to share risk management know-how within the company. Young PMs can also learn much risk management experience and techniques from the company's knowledge base, to improve project management.
With regard to risk identification, data can be created by referring to the three patterns of "risk standard data", "past project data" and "new construction". It can not only identify risks easily, but also save login time.
With regard to risk assessment and monitoring, who did what and how the risk status was, the traces of change could be regularly recorded. In addition, as soon as the risk occurs, it will be transformed into a subject, and it is also convenient to trace the solution along the road of subject management.